Modern visual restoration operations are high -tech and safe procedures that allow us to eliminate almost any ophthalmic problem.They have been successfully used for several decades, so the methods are constantly developing, expanding and becoming more effective.Improving visual functions is achieved using hardware correction of the shape of the cornea, lens, retina and other elements of the optical system of the eye.Properly selected technology allows not only to completely restore vision, but also to reduce the risk of complications.From the article you will learn what ophthalmic operations, indications for use and possible risks exist.
Types
Thanks to the development of hardware methods of medicine, visual and minimally invasive procedures are reliable and minimally invasive.Their duration does not exceed several hours, and in the future there is no need for complex rehabilitation measures.The choice of surgical treatment method is chosen depending on the disease, age and general condition of the patient's visual apparatus.
Laser correction
The most popular type of operation to correct visual acuity.Today these are honed high -tech methods that have high efficiency and minimal risk of complications.Allow you to cope with myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism.After the procedure, visual acuity is maintained for a long time, and if you follow all the instructions of an ophthalmologist, you can completely avoid repeated intervention.There are several types of laser correction:
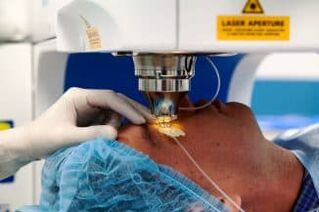
- Lasik.The basic type of operation to restore visual acuity.First, the surface layer of the cornea is separated by a microcarata, and then, using a laser ray, a change in its shape is carried out.The main disadvantage of this type of correction is the inability to take into account the individual characteristics of the patient's eye anatomy;
- Super Lasik.An advanced version of the traditional LASIK methodology.Allows you to achieve a better result, as it takes into account the structure of the visual system of the patient.Used in most modern clinics in the world;
- Femto Lasik.A similar type of operation, the only difference is that the cut of the cornea is carried out not by a microcarat, but by a special femo laser.There is an improved version in which the course of the operation depends on the individual characteristics of the patient - Super Femto Lasik;
- Epi-Lasik.The mechanism of the procedure is identical to the traditional LASIK method, but such an operation is prescribed only to patients with an thinned cornea (acquired or congenital);
- PRK (FRK).Photo refraction keratectomy has been carried out since 1985.Today it is applied in the presence of contraindications to ordinary correction methods, for example, with a subtle cornea, serious ophthalmic diseases.The healing process is always painful, the recovery period lasts longer than in other methods.
Visual correction operations last no more than 15 minutes.After the procedure, wearing a protective dressing for several hours, as well as instillation of drops for 1-2 months, is necessary.The risk of complications is minimal, repeated treatment is necessary with a significant decrease in vision.
Vitrectomy
This is a procedure for complete or partial removal of the vitreous body of the eyeball.It is carried out under general or local anesthesia, in the absence of complications, it passes in 2-3 hours.First, small punctures are made in the eye socket, through which subsequent manipulations are carried out.As a rule, this is a cauterization by a laser of the affected areas of the retina, the densification of abroad, or the restoration of fabric integrity.The procedure is prescribed for the following problems:
- restoration of visual functions after hemorrhage in the tissues of the eye;
- prevention of age -related retinal detachment;
- Treatment of severe retinopathy of the eyes in which gross scars or neovascularization (germination of blood vessels) occur.
Artificial polymers, gas bubble, silicone oil or a balanced solution of salt are used as a replacement for the vitreous body.The latter type is used more often, since in the future a repeated operation is not required - the salt solution is subsequently replaced by intraocular fluid.
After surgery, side effects are possible in the form of swelling of the cornea, increasing intraocular pressure, or even more vision.Restoration and forecast depend on the vastness of the lesion, as well as the type of prosthesis when replacing the vitreous body.If there are irreversible changes in the optic nerve, then vision correction is almost impossible.
Scleroplasty
A common ophthalmic procedure aimed at strengthening the outer shell of the eye (sclera).It is prescribed not to correct visual functions, but to stabilize the degree of myopia in the patient from the risk group.It is recommended to be carried out by adolescents suffering from this problem, since at this age the shape of the eye is actively changing.
During the operation, the required amount of material flaps to strengthen the sclera is introduced behind the back wall of the eyeball.Polymers or biological components are usually used.After that, a spike occurs with the outer shell of the eye, and after a few months the blood vessels necessary to maintain visual functions grow into the flap.There is a simplified version of scleroplasty.It is an introduction of an artificial or biological substance for the eyeball.The mechanism of action in such a technology is identical - preventing the growth of the eyeball.
Scleroplasty
This is a well -studied operation that practically does not change over the years.It is carried out in most clinics.There were practically no side effects, with the exception of possible allergies to the drug.A second operation is usually required.
Replacing the lens
The necessary operation, which is prescribed during clouding or any other degenerative processes in the lens, for example, cataracts.The treatment is always forced, but the implant is selected individually, depending on the age, gender and the severity of pathological changes in the eye.Crystalus replacement is prescribed in the following cases:
- high degrees of myopia and farsightedness;
- significant decrease in refraction;
- regenerative processes in the eye, age -related decrease in vision;
- the impossibility of laser vision restoration;
- cataract;
- The probability of developing glaucoma against a background of a systemic or ophthalmic disease.
The procedure always takes place under local anesthesia.During the operation, the surgeon makes a small incision with a laser, after which the patient's lens dilutes with a special tool and removes him from the eye.After that, a prepared transplant is installed.The intervention lasts no more than 25 minutes, the subsequent imposition of seams and recovery in the hospital is not required.
The operation is carried out in most private and state clinics.There are usually no complications after manipulation, but the subsequent laser vision correction is often prescribed.In rare cases, a re -replacement of the lens is necessary.
Keratoplasty (replacement of cornea)
One of the most modern and complex ophthalmic operations, which is associated with many risk and requires a high qualification of the surgeon.It is required to restore the anatomical integrity and physiological functions of the cornea.It is prescribed for the treatment of congenital or acquired defects obtained as a result of injuries or diseases.Healthy fabric for transplantation is taken only in donors, but the development of artificial replacement is carried out in many countries.Keratoplasty is recommended to solve the following problems:
- Treatment of corneal diseases (belko, tone disturbances);
- mechanical or chemical damage;
- Congenital defects.
The operation is carried out no more than 30 minutes.During the procedure, the surgeon with a laser or special scalpel removes part of the patient’s cornea, and implants donor fabric in its place.The seams can persist up to a year, after which a special lens is selected to reduce the risk of infections.The recovery period is from 4 weeks, during which the antibiotic is needed, but regular examinations are required for the entire subsequent year.
In recent years, it was possible to significantly reduce the risk of rejection of donor fabric due to the use of special compositions during its processing and preservation.
Laser coagulation of the retina
The operational method of restoration of retinal tissue.The effectiveness of the method is more than 70%, and already 24 hours after its implementation, you can return to the usual lifestyle.Observations by an ophthalmologist are necessary within a year after the procedure.
Today, the operation is carried out using a laser, which allows you to do without loss of blood.Anesthesia is carried out under local, the procedure time takes no more than 20 minutes.
Before exposure to the laser, drip drops to expand the pupil, and then put on a special protective lens, through which exposure occurs at low frequencies.Due to high temperatures, gluing damaged cells, as well as small blood vessels.
The coagulation procedure is necessary for any damage and pathologies of the retina, as well as with eyes and diseases of the vascular system of this organ.After the operation, inflammation and clouding is possible.For several years after correction, it is impossible to engage in heavy physical labor and active sports.
Crosslinking
An effective method of treating various diseases of the cornea.It is carried out to strengthen ligaments and other fibers in corneal tissues, which is necessary for keratoconus of varying degrees or degenerative processes, dystrophy.
The operation is carried out under local anesthesia.First, a small part of the cornea is cut off with a special device, and vitamin B2 is instilled into the open area.Subsequent irradiation allows you to compact fabrics by more than 200%.The first week after the operation, it is necessary to wear a protective contact lens, and for 6 months to be examined by a doctor.The effect of the procedure persists for 10 years, then a repeated operation is required.
Complications are observed in rare cases.The patient may decrease vision, inflammation or clouding of the cornea may occur.
Treatment of glaucoma
The ophthalmological operation for various degrees of glaucoma is necessary when drug therapy does not bring the necessary result.The operation is carried out using a laser or surgically.
The laser method is considered the most successful.He is completely painless for the patient, and there are practically no complications.During the procedure, a hole is made with a beam through which the liquid is removed from the tissues of the eye to normalize pressure.It is used to treat all types of glaucoma.
The manual surgical type of operation is less effective because there is a risk of complications after the procedure.As a rule, this is a non -praying deep sclerectomy.The purpose of the method is to reduce intraocular pressure using a slight thinning of the corneal layer.
The effect after both types of operations is reduced over time.On average, after 5-7 years, a second operation is required.This period can be extended using competent drug treatment.
Conclusions
Today, in most modern ophthalmic clinics, a number of surgical procedures are carried out for vision correction.These are accurate high -tech methods with which you can solve almost any eye defect.The choice of the method depends on a number of factors - age, disease, individual characteristics of the structure of the visual system of the patient.After the operation, the effect occurs almost immediately, and if all the doctor’s prescriptions are observed, visual acuity can be preserved for a long time.